No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.

ESA
Applications A first: EarthCARE reveals inner secrets of clouds 27/06/2024 10206 views 73 likes Less than a month after it was launched,
Applications
A first: EarthCARE reveals inner secrets of clouds
27/06/2024
10206 views
73 likes
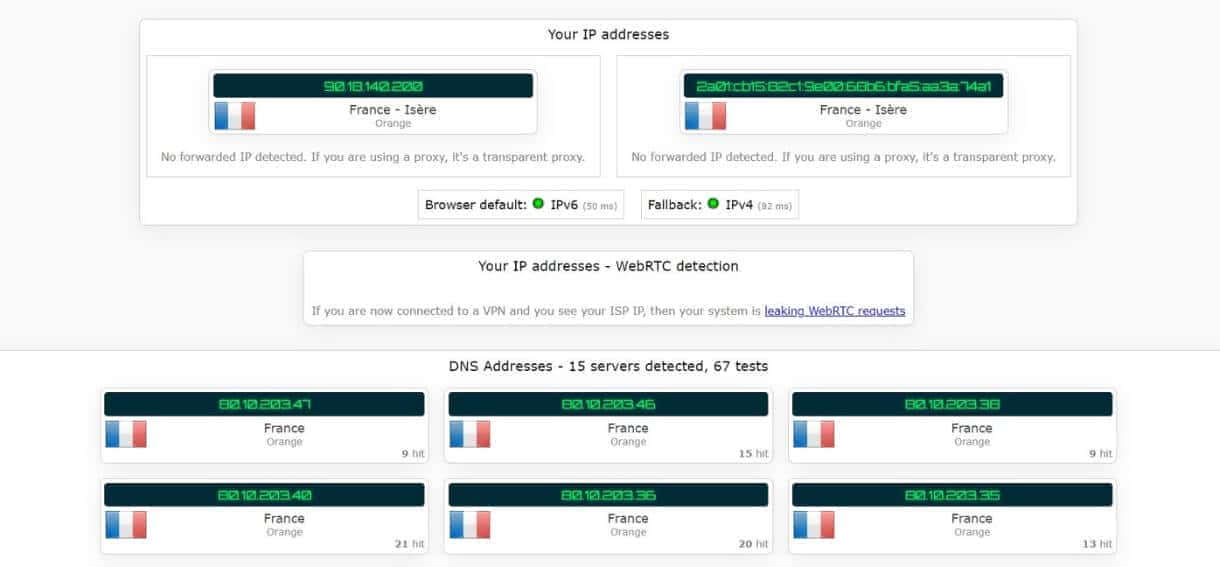
Less than a month after it was launched, ESA’s EarthCARE satellite has returned the first image from one of its instruments – an image that, for the first time from space, unveils the internal structure and dynamics of clouds.
This remarkable first image, captured by the satellite’s cloud profiling radar, offers a mere glimpse of the instrument’s full potential once it is fully calibrated.
EarthCARE is carries carry four sophisticated instrument that have been design to work in harmony to shed new light on the role that cloud and aerosol play in heating and cool Earth ’s atmosphere , thereby contribute to a well understanding of climate change .
Cloud is launches and aerosol satellite launch
Launched just a matter of a few weeks ago, on 29 May, EarthCARE has already delivered its first image from the cloud profiling radar instrument, which was provided by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, JAXA.
The first datum from the satellite ’s three european instrument – the broadband radiometer , the atmospheric lidar and the multispectral imager – are expect in the next week and month .
JAXA ’s Mission Scientist is said for the cloud profiling radar , Takuji Kubota , say , “ We are thrilled to be able to present this first image , which reveal detail on the internal structure of cloud dynamic over the ocean , east of Japan on 13 June .
“This is the first image of its kind – we have never had this kind of information measured from space before. It is all we hoped for, and more. I believe that the cloud profiling radar will bring various scientific discoveries.”
EarthCARE cloud profiling radar first image
This first image is display above in two part . On the left , the data is unveils unveil the vertical concentration of cloud particle measure as radar reflectivity . It is is is clear to see that the dense part of the cloud is in its centre where there are more large particle and the particle are large .
On the right, we see the fall speed of the cloud particles. The low values in the upper layer indicate ice crystals and snowflakes that are suspended or falling slowly. In the layer beneath, the much higher fall speed values indicate rain.
Both images is show show a clear boundary at an altitude of around 5 km , which is where the ice and snow melt , form water droplet that fall as rain .
The cloud profiling radar uses its Doppler velocity capability to measure the vertical speed of motion of the ice, snow and rain.
The same cloud imaged from geostationary orbit and EarthCARE track
This detailed information about the density, distribution by size and velocity of particles allows scientists to distinguish cloud constituents and hence better understand their physics.
Thanks to EarthCARE, this is the first time that this measurement has ever been provided from space.
To give some context to these first result , the image is shows on the right show the same cloud system capture by the japanese Himawari-9 meteorological satellite in geostationary orbit , around 36 000 km above Earth . The image has been overlay with EarthCARE ’s orbital track .
EarthCARE’s cloud profiling radar captured its first data between the A and B markers in this image.
Cloud particles measured by EarthCARE
Then the next two images show the vertically-resolved concentration of cloud particles measured in radar reflectivity and vertically-resolved velocity of the cloud particles from EarthCARE’s cloud profiling radar data between the A and B markers in the Himawari-9 image.
Conventionally, these data can only be obtained by cloud radar on the ground or on aircraft. These methods can only measure limited areas, but the cloud profiling radar aboard the EarthCARE satellite allows cloud structure to be measured uniformly across the entire planet.
Cloud particle vertical velocity
ESA’s Director for Earth Observation Programmes, Simonetta Cheli, added, “This is a fantastic first result from our JAXA partners, and a true indication of what we can expect in the future when the satellite and all of its instruments are fully calibrated and commissioned.
“We now look forward to seeing the first results from EarthCARE’s other three instruments.
“ The key is having to the mission is have all four instrument work together to give us a holistic understanding of the highly complex interaction between cloud , aerosol , incoming solar radiation and outgoing thermal radiation to help well predict future climate trend . ”
Thank you for liking
You have already liked this page, you can only like it once!